Power Converter
The Power Converter tool allows you to convert between different units of power, such as watts, kilowatts, horsepower, and more, providing accurate and instant results. This tool is perfect for engineers, electricians, students, and anyone who needs to convert power measurements for various applications. The process is user-friendly and efficient, ensuring precise conversions every time.
Share on Social Media:
Understanding Power Converters: A Comprehensive Guide by PagesTools.com
Power converters are essential devices in various industries, enabling the transformation of energy from one form to another. They play a crucial role in ensuring that power is efficiently and effectively utilized in different applications. PagesTools.com offers a versatile power converter that supports a wide range of units, making it a valuable tool for engineers, scientists, and technicians. This article delves into the specifics of the power units available in the PagesTools.com converter, providing a detailed understanding of each unit and its application.
BTU (SI)/hour
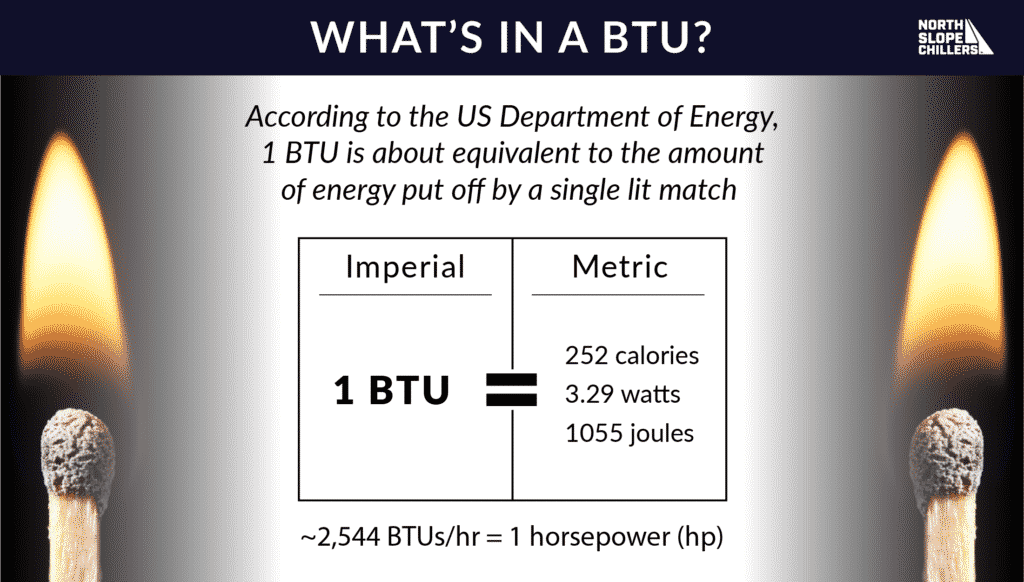
The British Thermal Unit (BTU) is a traditional unit of heat, defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. When measured in BTU (SI)/hour, it represents the rate at which energy is transferred, equivalent to approximately 1.055 kW. This unit is commonly used in heating and cooling applications, such as in HVAC systems, to specify the heat output or cooling capacity of equipment.
BTU (thermo)/hour
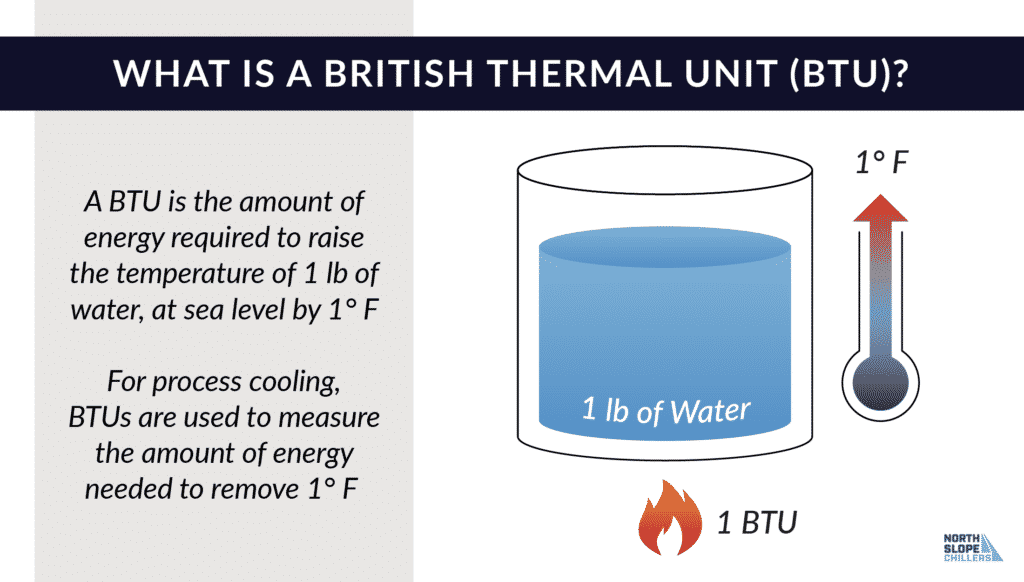
Similar to BTU (SI)/hour, the BTU (thermo)/hour is a unit of power based on the thermochemical calorie. It is slightly larger than the BTU (SI), with one BTU (thermo) equal to 1.05506 kW. This unit is frequently used in thermodynamics and engineering contexts, particularly in the United States.
BTU (thermo)/minute
The BTU (thermo)/minute is a unit of power indicating the rate of energy transfer per minute. It is often used in applications where rapid heating or cooling is essential, such as in industrial processes or high-performance HVAC systems. Converting BTU (thermo)/minute to other units can help engineers optimize system performance.
BTU (thermo)/second
For even more precise energy transfer rates, BTU (thermo)/second is used. This unit is critical in applications requiring exact measurements of power output, such as in laboratory experiments or detailed engineering calculations. It provides a direct measurement of the energy transfer per second, facilitating accurate and efficient system design.
Calorie (thermo)/minute
The calorie is a unit of energy, commonly used in food and nutrition. When measured as Calorie (thermo)/minute, it denotes the rate of energy transfer in calories per minute. This unit is useful in biological and chemical processes where energy transfer rates need to be quantified, such as in metabolic studies or chemical reactions.
Calorie (thermo)/second
Similar to Calorie (thermo)/minute, the Calorie (thermo)/second unit measures the rate of energy transfer per second. This unit is particularly useful in high-precision scientific experiments and industrial processes where rapid energy changes are observed and need to be accurately measured.
Erg/second
The erg is a unit of energy in the centimeter-gram-second (CGS) system. When expressed as erg/second, it denotes the rate of energy transfer in ergs per second. This unit is commonly used in physics, particularly in areas like electromagnetism and mechanics, where small energy transfers are studied.
Foot-pound force/hour
The foot-pound force is a unit of work or energy in the English engineering system. When measured as foot-pound force/hour, it indicates the rate of energy transfer in foot-pounds per hour. This unit is often used in mechanical engineering, particularly in the study of mechanical systems and their energy requirements.
Foot-pound force/minute
Similar to foot-pound force/hour, the foot-pound force/minute unit measures the rate of energy transfer per minute. This unit is useful in applications where mechanical work is performed over shorter time intervals, such as in machinery operations and mechanical testing.
Foot-pound force/second
The foot-pound force/second unit measures the rate of energy transfer per second, providing a precise measurement for high-speed mechanical processes. This unit is essential in engineering fields where rapid energy transfer needs to be accurately quantified, such as in the design of engines and turbines.
Horsepower (UK)
Horsepower (UK) is a unit of power traditionally used in the United Kingdom. One horsepower is equivalent to approximately 745.7 watts. This unit is commonly used to rate the power output of engines and motors, providing a familiar measure for engineers and mechanics.
Horsepower (boiler)
Horsepower (boiler) is a unit of power used to measure the output of steam boilers. One boiler horsepower is equivalent to the energy required to evaporate 34.5 pounds of water per hour at 212 degrees Fahrenheit. This unit is crucial in the design and operation of steam boilers, ensuring that they operate efficiently and safely.
Horsepower (electric)
Electric horsepower is a unit of power used to rate electric motors and other electrical equipment. One electric horsepower is equivalent to approximately 746 watts. This unit is widely used in electrical engineering, providing a standard measure for the power output of electric devices.
Horsepower (metric)
Metric horsepower is a unit of power used in many countries outside of the United States. One metric horsepower is equivalent to approximately 735.5 watts. This unit is commonly used to rate the power output of engines and motors in automotive and industrial applications.
Horsepower (550 ft lbf/s)
This unit of horsepower is based on the definition of one horsepower as 550 foot-pounds of force per second. It is a traditional unit used in mechanical and automotive engineering, providing a measure of the power output of engines and other mechanical systems.
Kilocalorie (thermo)/minute
The kilocalorie (thermo)/minute unit measures the rate of energy transfer in kilocalories per minute. This unit is useful in applications where large amounts of energy are transferred rapidly, such as in industrial processes and high-performance HVAC systems.
Kilocalorie (thermo)/second
Similar to kilocalorie (thermo)/minute, the kilocalorie (thermo)/second unit measures the rate of energy transfer per second. This unit is essential in scientific experiments and industrial processes where precise measurements of rapid energy transfer are required.
Kilowatt (kW)
The kilowatt is a widely used unit of power, equivalent to 1,000 watts. It is commonly used to rate the power output of engines, motors, and electrical equipment. The kilowatt is a standard unit in electrical engineering, providing a familiar measure for the power consumption and output of various devices.
Megawatt (MW)
The megawatt is a unit of power equivalent to 1,000 kilowatts or one million watts. This unit is commonly used in the power generation industry to measure the output of power plants and other large-scale energy systems. It provides a convenient measure for the large amounts of power generated and consumed in modern energy systems.
Milliwatt (mW)
The milliwatt is a unit of power equivalent to one-thousandth of a watt. This unit is commonly used in electronics and telecommunications to measure the power output of small devices, such as sensors and transmitters. The milliwatt provides a precise measure for low-power applications, ensuring that devices operate efficiently and effectively.
Applications and Importance of Power Converters
Power converters are indispensable in a wide range of applications, from industrial processes and power generation to scientific research and everyday household appliances. They ensure that energy is converted and transferred efficiently, minimizing losses and maximizing performance. The versatility of the PagesTools.com power converter, with its extensive range of units, makes it an invaluable tool for professionals across various fields.
For instance, in the HVAC industry, power converters are used to measure and optimize the performance of heating and cooling systems. Accurate measurements of BTU (SI)/hour or BTU (thermo)/hour can help engineers design systems that provide optimal comfort while minimizing energy consumption. Similarly, in the automotive industry, units like horsepower (metric) and horsepower (550 ft lbf/s) are crucial for rating the power output of engines, ensuring that vehicles perform reliably and efficiently.
In scientific research, precise measurements of power are essential for experiments and simulations. Units like Calorie (thermo)/second and Erg/second provide the accuracy needed for high-precision experiments, enabling scientists to study energy transfer and conversion processes in detail. In the power generation industry, units like kilowatt (kW) and megawatt (MW) are used to measure the output of power plants, ensuring that they operate efficiently and meet the energy demands of modern society.
Conclusion
Power converters are vital tools in various industries, enabling the efficient and effective transformation of energy. The PagesTools.com power converter, with its extensive range of units, provides a versatile and accurate solution for professionals across different fields. Understanding the different units available in the converter, from BTU (SI)/hour to milliwatt (mW), allows for precise measurements and optimized performance in various applications. Whether in industrial processes, scientific research, or everyday applications, power converters play a crucial role in ensuring that energy is used efficiently and effectively.